Katy, Spring, The Woodlands, Mont Belvieu Impacted
An analysis of thousands of water and oil wells in the Houston metro area has uncovered significant rates of subsidence, or gradual sinking of the ground, in some of the region’s fast-growing suburbs that have not been previously reported.
Shuhab Khan, professor of geology at the University of Houston, led the study published in the academic journal Remote Sensing. His team found substantial subsidence in Katy, Spring, The Woodlands, Fresno and Mont Belvieu with groundwater and oil and gas withdrawal identified as the primary cause.

“Subsidence used to be a rare phenomenon. Now, it is all over the world,” said Khan, who is on the UH College of Natural Sciences and Mathematics faculty. “There are 200 locations in 34 countries where there’s known subsidence. Cities in the northern Gulf of Mexico, such as Houston, have experienced one of the fastest rates of subsidence.”
Severe subsidence not only raises the possibility of flooding homes and businesses, but it also produces a negative feedback loop, the study authors write. The weight of floodwater from severe flooding can compress the sediments in the subsurface and could exacerbate the already compacted soil to potentially drive subsidence further.
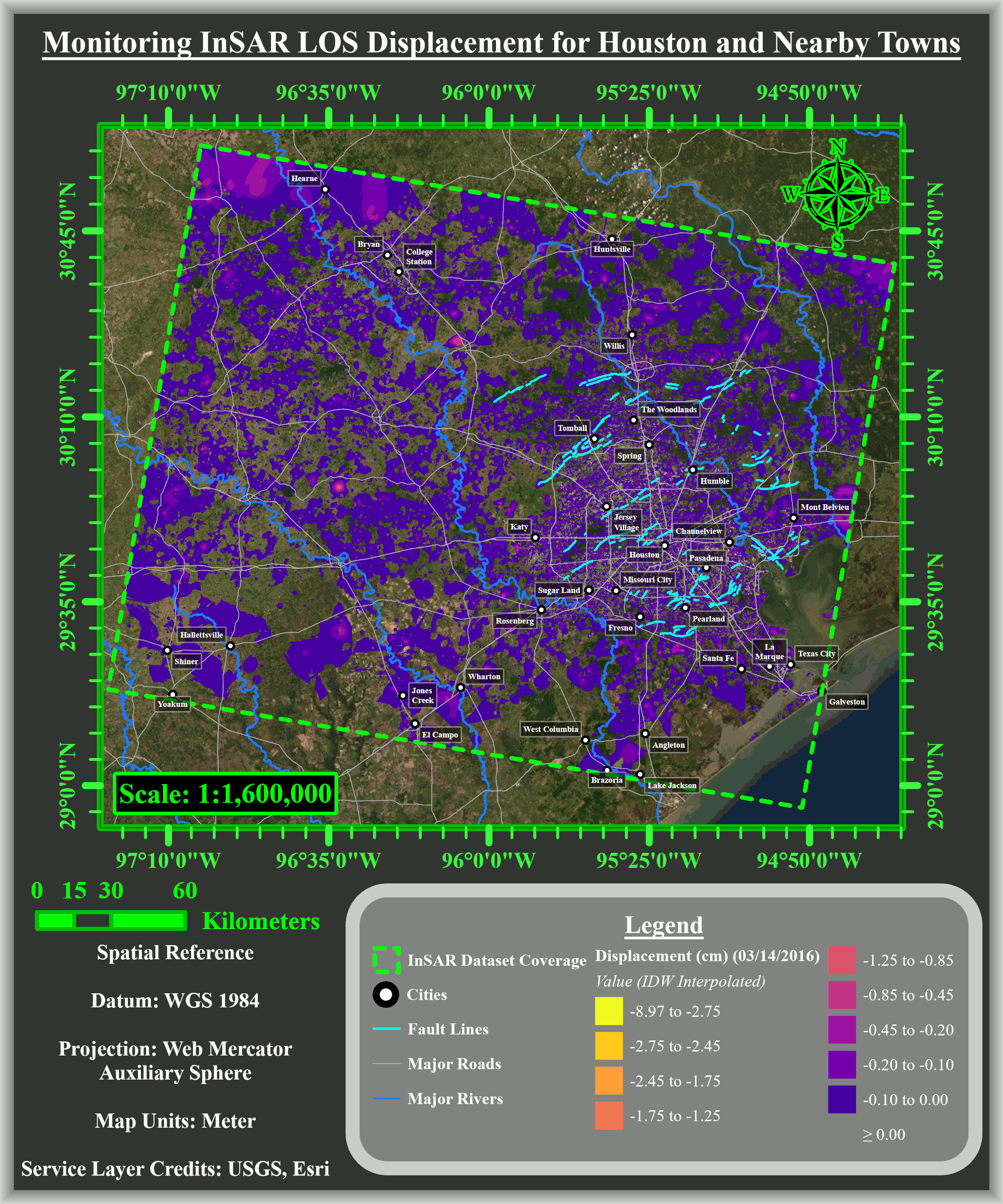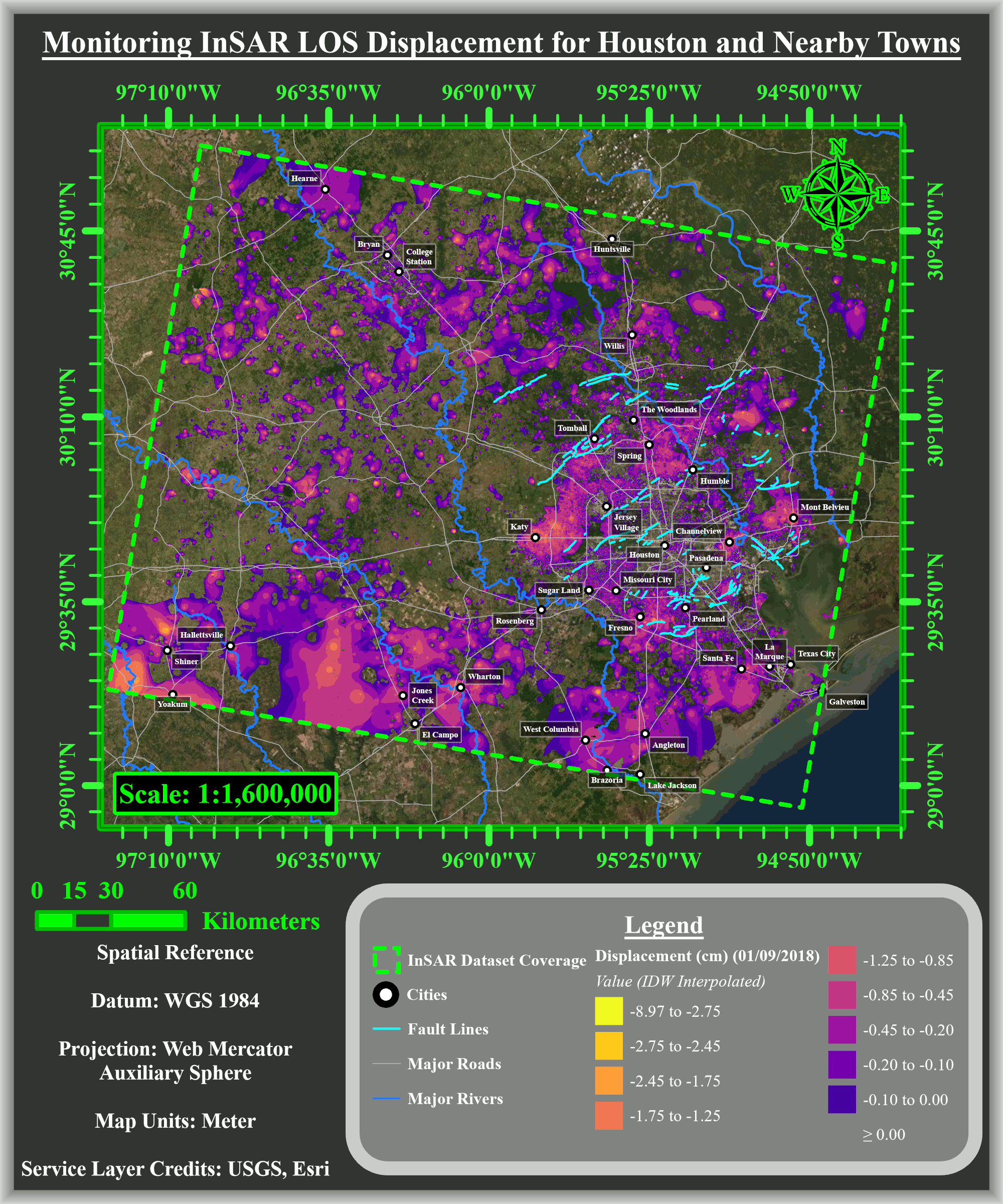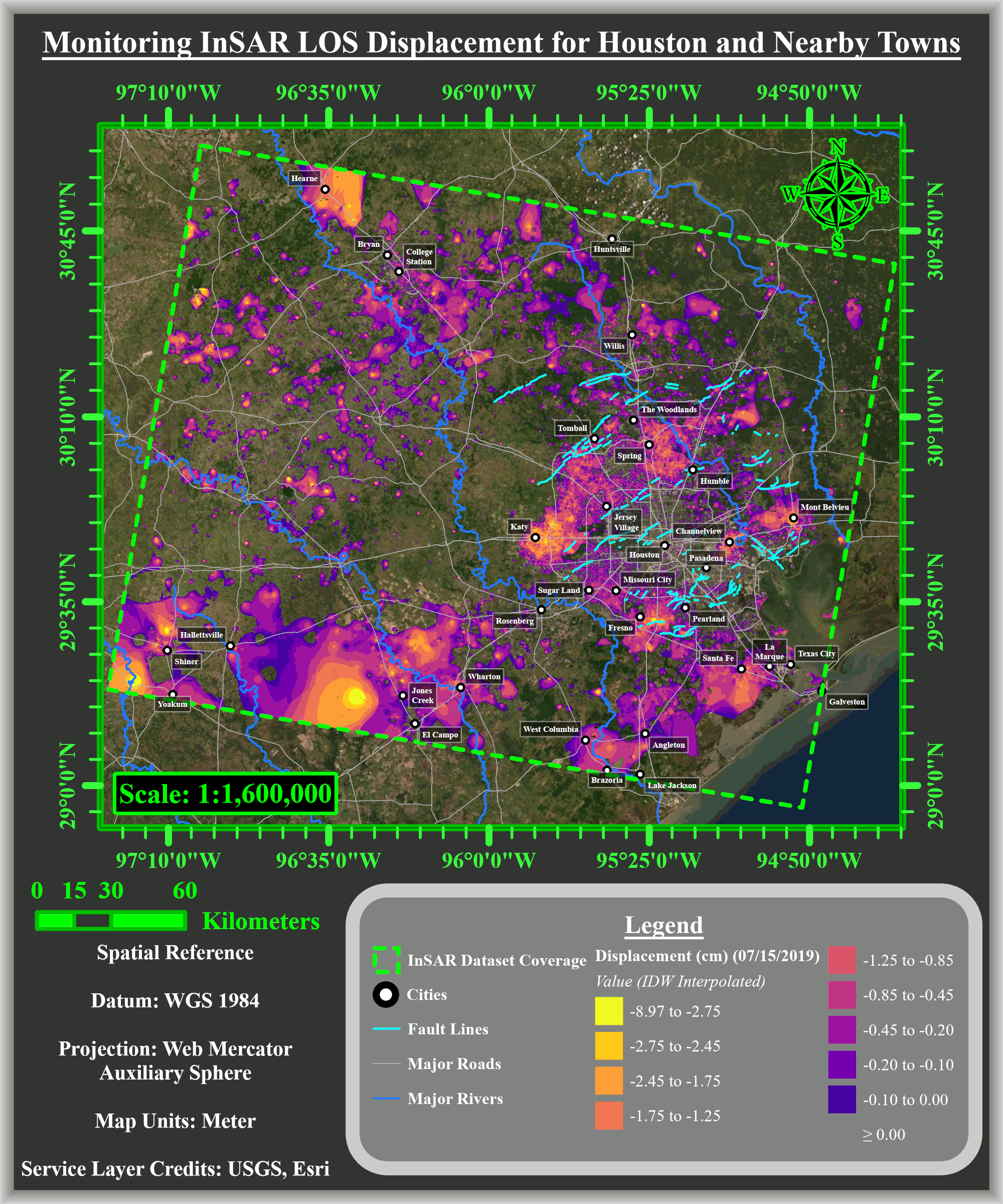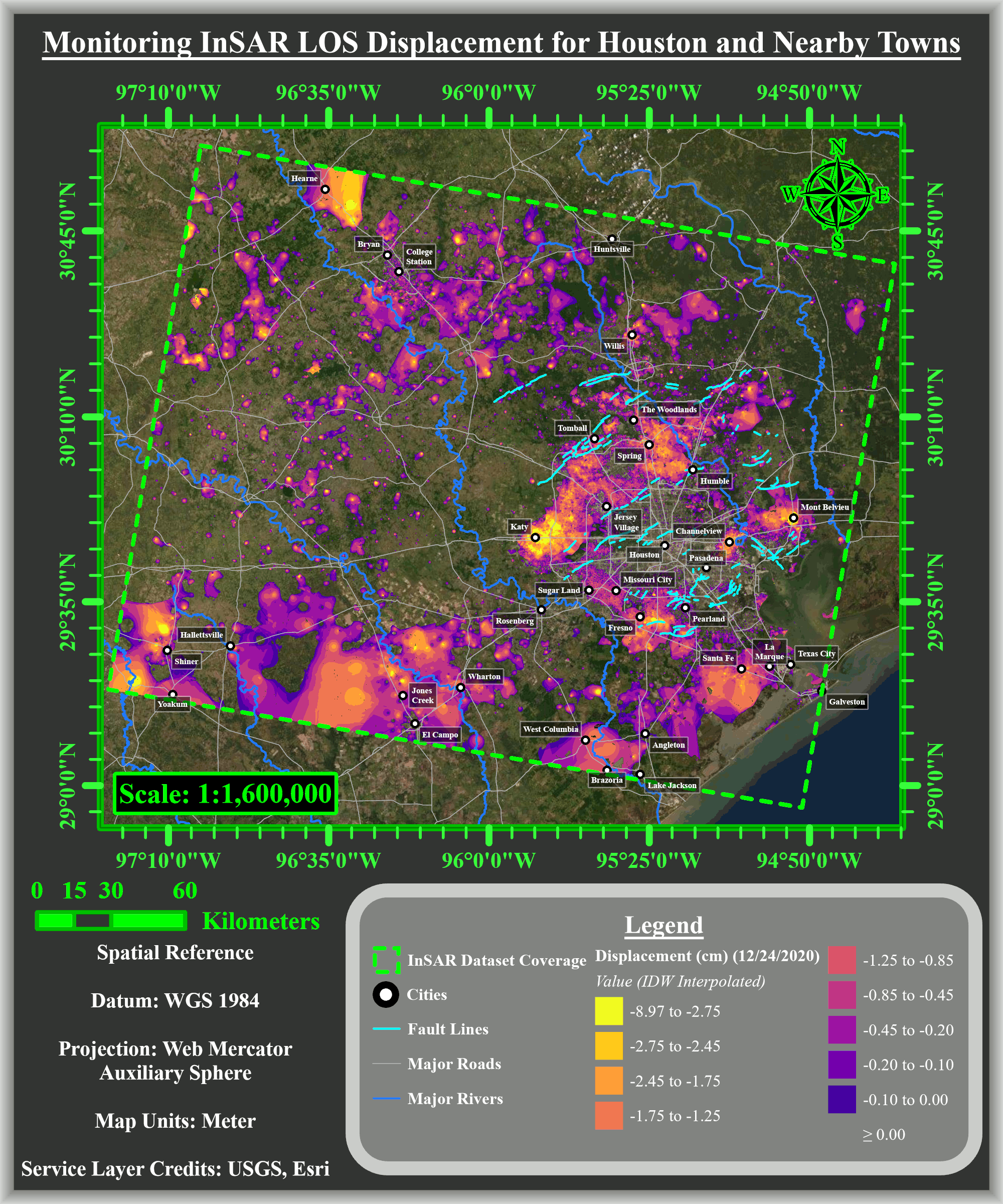
The researchers used interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) data obtained from a European Space Agency satellite, which showed total subsidence of up to 9 cm to the north, northwest and west of Houston from 2016 to 2020. The subsidence rate was 2 cm a year.
Khan and his team applied optimized hot spot analysis, a statistical tool, to groundwater level data collected over the past 31 years from more than 71,000 water wells to consider how much groundwater pumping contributed to subsidence. Similarly, they used the same analysis on more than 5,000 oil and gas wells to evaluate their impact on subsidence.
“It is thanks to the latest advances in geospatial analysis that we were able to investigate subsidence across the Houston area in unprecedented detail,” said Otto Gadea, a graduate student from Khan’s team. “By analyzing comprehensive datasets from recent years, we determined for the suburbs, excessive groundwater extraction appears to be the primary driver of subsidence. Meanwhile for other areas such as Mont Belvieu, subsidence can be attributed to the heavy withdrawal of local oil and natural gas reserves.”
With population growth, groundwater extraction has become more prevalent in the Houston area. Khan points out downtown Houston, suburbs to Houston’s southeast and parts of Spring Branch previously experienced subsidence, but because of groundwater regulation, the subsidence is no longer substantial.
His team also studied natural causes for the sinking, like the expansion and shrinking of Houston’s clay, silty and sandy soil sediments, and the impact of flooding. Sinking may also be causing fault movement in the area.
“If current ground pumping trends continue, faults in Katy and The Woodlands will likely become reactivated and increase in activity over time,” the authors write.
- Rebeca Hawley, University Media Relations