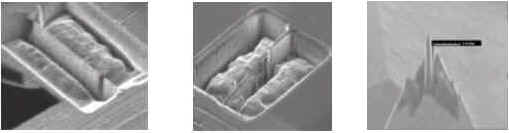
Nanomagnetic transducers fabricated focused ion-beam (FIB). Left to right: 30nm wide longitudinal writer;
60nm wide perpendicular writer; ultra-sharp probe transducer with 40nm x 40nm x 10nm apex.
The current research activities are focused on applications of nanocrystalline materials and nanoscale devices for achieving extremely high density recording (above 1Terabit/in 2 ). The current state-of-the-art in magnetic recording is 160x40x10nm magnetic features (corresponding to areal density of 100Gbin/in 2) recorded into a magnetic recording medium. The individual magnetic grains forming the recording medium are ~9nm in diameter. At these dimensions, the conventional recording schemes employed today are rapidly approaching the fundamental (superparamagnetic) limit in areal bit density, above which the recording data become unstable. It is widely believed that longitudinal recording will run out of steam at approximately 200Gbin/in 2 . Perpendicular magnetic recording will enable to sustain the current great strides in technological advances for the next several generations of mass storage solutions. The technology is technically the closest alternative to conventional longitudinal recording, while it is capable of extending the superparamagnetic density limit beyond what is achievable with longitudinal recording. The recording densities above 1Terabit/in 2 (recording features as small as 50x12x10nm) are conceivable utilizing perpendicular recording. To support such a nanoscale technology, major innovations in both magnetic recording heads and media are necessary.
- D. Litvinov and S. Khizroev , "Orientation-Sensitive Magnetic Force Microscopy for Future Probe Storage Applications," Applied Physics Letters 81(10), 1878-1880 (2002) [Editor's choice in the AIP Virtual Journal of Nanoscience & Technology, Vol. 6(11), Sept. 2002].
- S. Khizroev, D.A. Thompson, M.H. Kryder, D. Litvinov, "Direct Observation of Magnetization Switching in Focused Ion-beam Fabricated Nanotubes," Applied Physics Letters 81(12), 2256-2257 (2002) [Editor's choice in the AIP Virtual Journal of Nanoscience & Technology, Vol. 6(12), Sept. 2002].
- D. Litvinov and S. Khizroev, "Focused Ion Beams in Future Nanoscale Probe Recording," Nanotechnology 13, 179-184 (2002).
- D. Litvinov and S. Khizroev , "Overview of Magnetoresistive Probe Heads for Nanoscale Recording Applications," Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 264(2-3), 275-283, 2002.
- J.T. Wolfson, J.A. Bain, S. Khizroev , and D. Litvinov, "Dynamic Kerr Imaging of Soft Underlayer for Perpendicular Recording Applications," (invited) Journal of Applied Physics 91(10), 8665-8669 (2002).
- D. Litvinov, J. Wolfson, J. Bain, R.W. Gustafson, M.H. Kryder, and S. Khizroev, "Narrow Gap Single Pole Heads," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 38(5), 2253-2255 (2002).
- D. Litvinov, M.H. Kryder, and S. Khizroev , "Recording Physics of Perpendicular Media: Hard Layers," Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 241(2-3), 453-465 (2002).
- D. Litvinov, J.Wolfson, J.A. Bain, R.W. Gustafson, M.H. Kryder, S. Khizroev, "The Role of the Gap in Single Pole Heads in Perpendicular Recording," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 38(4), 1658-1663 (2002).
- D. Litvinov, T. Roscamp, T. Klemmer, M. Wu, J.K. Howard, S. Khizroev , "Co/Pd Multilayers for Perpendicular Recording Media," MRS Proceedings 674, T3.9 (2001).
- D. Litvinov, R. Chomko, G. Chen, L. Abelmann, K. Ramstock, and S. Khizroev, "Micromagnetics of a Soft Underlayer," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 36(5), 2483 (2000).
ECE 3455: Electronics
ECE4339 : Physical Principles of Solid State Devices
ECE 5397/6397: Introduction to Design and Fabrication of Nanoscale Devices
ECE 6397: Fundamentals of Ferromagnetic Devices and Materials
Prof. Dmitri Litvinov
Electrical and Computer Engineering
Room N 308, Engineering Building 1
University of Houston
Houston, TX 77204-4005
Tel: 713-743-4168
Fax: 713-743-0544
E-mail: litvinov@uh.edu

