The Earth - An Introduction

Weathering
- Which is more dense....water or steam?
- water
- steam
- Which is more dense....ice or vapor?
- ice
- vapor
- If the pressure increases, what happens to the melting point of ice?
- increases
- decreases
- stays the same
- What happens to the boiling point of water as the pressure decreases?
- increases
- decreases
- stays the same
- At 1 atmosphere total pressure water cannot be heated above 100oC. At that temperature water is converted to steam (vapor). According to the diagram, water can be heated to higher temperatures by:
- increasing the pressure
- decreasing the pressure
- increasing the temperature
- Water from a certain source is shown to contain 10,000 ppm dissolved solids.
This indicates that what percentage (parts per 100 parts) of the particles in this water are represented by
the dissolved solids?
- 0.01%
- 0.1%
- 1.0%
- 10.0%
- Mechanical weathering produces:
- clay minerals
- quartz
- smaller particles
- calcium carbonate
- When liquid water freezes:
- it actually does not expand in volume
- it expands by 5% in volume
- it expands by 9% in volume
- it doubles in volume
Sedimentary Rocks
- Of the rocks found in the continental crust ______ is the most likely to change chemically?
- basalts
- andesties
- rhyolites
- Of the common minerals found in the continental crust ______ is the least likely to change chemically?
- quartz
- alkali feldspar
- plagiolclase feldspar
- olivine
- Which of the following minearals is not a source of clay minerals?
- quartz
- alkali feldspar
- plagiolclase feldspar
- olivine
- The term sandstone conveys information about:
- particle size
- particle composition
- particle size and composition
- The difference between a mudstone and a shale is:
- particle size
- particle shape
- particle composition
- particle orientation
- particle size and composition
- Shale refers to a rock formed from:
- sand
- plant remains
- clay minerals
- carbonate
- a brine
- Which one of the following is a biochemical sedimentary rock?
- sand
- sandstone
- coal
- shale
- a conglomerate
- A clastic rock is:
- a rock that contains groundwater
- a rock formed from the cementation of rock fragments
- a rock formed from evaporation
- transformed by heat and pressure into limestone
- any rock that can be burned for fuel
- Which one of the following features is NOT associated with sedimentary rocks?
- bedding
- foliation
- fossils
- ripple marks
- all may be associated with sedimentary rocks
Metamorphism
- In regional metamorphism the source of increased temperature and
pressure is:
- local igenous heat source
- impact metamorphism
- increasing depth of burial
- A combination of shallow earthquakes, tension, and contact
metamorphism characterizes:
- local igenous heat source
- transform fault margins
- spreading centers
- continent/continent margins
- A Geologist suffers from a black eye after yelling "Gneiss!!!" to a
classmate, who happened to be sunning on a large boulder. The
geologist really meant to tell the classmate that the rock they were
laying on:
- would fizz with the application of acid
- is commonly used in billiard table construction
- demonstrates schistosity
- is a high-grade, silicate-rich metamorphic rock
- In contact metamorphism there is a:
- local heat source
- regional heat source
- very high pressure
- Within a 50 mile traverse you walk from a shale into a slate into a phyllite. You are walking in the direction of:
- increasing metamorphic grade
- decreasing metamorphic grade
- increasing degree of contact metamorphism
- Which of the following sedimentary rocks is least likely to exhibit mineralogical changes during regional metamorphism?
- limesones
- shales and mudstones
- quartz arenite
Geologic Times
- Atoms of AA decay to atoms of BB with a half-life of 100,000 years. If there are 20,000 atoms of AA to begin with (and 0 atoms of BB), how long will it take for there to be 2,500 atoms of AA?
- 100,000 years
- 200,000 years
- 300,000 years
- In the past there were (more or less) atoms of radioactive Uranium?
- less
- more
- cannot tell
- Therefore, there was (more or less) heat produced in the crust in the past:
- less
- more
- cannot tell
- Which era represents the longest time period
- Precambrian
- Paleozoic
- Mesozoic
- Cenozoic
- The Paleozoic does not include the
- Ordovician
- Jurassic
- Mississippian
- Permian
- The _________ was an era dominated by the dinosaurs
- Precambrian
- Paleozoic
- Mesozoic
- Cenozoic
- The boundaries between _______ seem to coincide with major changes in the life forms present on Earth.
- periods
- systems
- eras
- epochs
Deformation
- Material which fails while undergoing elastic behavior fails in a:
- brittle fashion
- plastic fashion
- spastic fashion
- folds
- Material which fails while undergoing plastic behavior fails in a:
- brittle fashion
- plastic fashion
- spastic fashion
- folds
- Look at the two folds in the illustration at the beginning of this chapter. These are:
- monoclines
- synclines
- anticlines
- homoclines
- Take four pieces of paper. Label the bottom one A, the next one B and so on.
In an undisturbed sequence which one represents the oldest rock layer?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- Now fold these units into an anticline with a vertical axial plane and limbs dipping in equal but opposite directions.
Imagine that erosion levels off this structure and you walk across it. Where are the oldest rocks?
- in the center or core
- on the limbs
- If you make a syncline and erode it, where are the oldest rocks - ?
- center or core
- limbs
- Create a recumbent fold. Imagine that erosion has leveled the structure so that the top half is eroded away. What has happened to bed A?
- bed A is at the bottom of the stack
- bed A is at the top of the stack
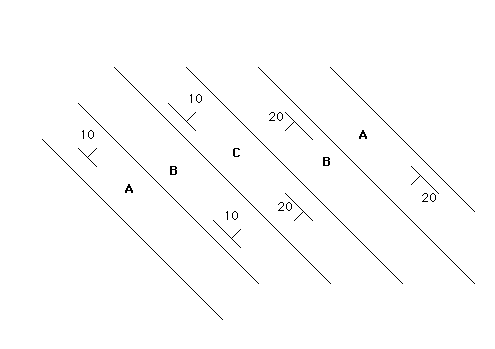
- In the map above North is to the top. The stike of the beds is about:
- north-south
- east-west
- about 45 degrees west of north
- about 45 degrees east of north
- The structure represented is a (an):
- symmetrical syncline
- asymmetrical syncline
- symmetrical anticline
- asymmetrical anticline
- The oldest unit is _______.
- A
- B
- C
- D
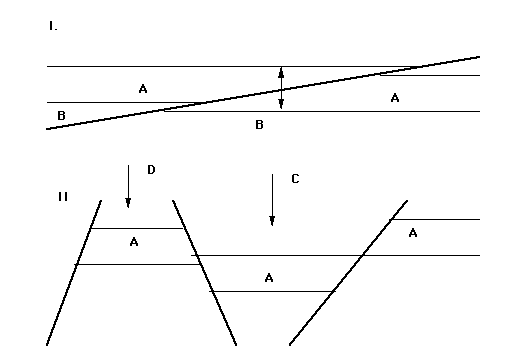
- In figure I a ________ fault is depicted (assume this is a dip slip fault)
- reverse
- thrust
- normal
- strike slip
- The fault in the figure above was produced by:
- compression
- tension
- shear
- The faults in figure II are:
- normal
- reverse
- both normal and reverse
- Structure C is a:
- horst
- graben
- ophiolote
- Structure D is a:
- horst
- graben
- ophiolote
Mass Wasting
- The most important stress opposing a slope's shear stress is imparted by:
- running water
- earthquakes
- frost wedging
- gravity
- Water can encourage mass flow by:
- reducing friction between grains
- undercutting a steep slope
- weathering bedrock to clay minerals
- all of the above
- Talus cones result from:
- rock fall
- rock glides
- mud flows
- all of the above
- One of the most effective ways to stabilize a slope is to:
- remove all excess vegetation
- increase the rate of compaction - add water
- control and remove water
- none of these
Groundwater
- The ability of an Earth material to transmit water is a measure of its:
- porosity
- aquifer characteristics
- chemical cement
- permeability
- lithification
- The lowering effect on the water table about the base of the well stem is called a:
- aquiclude
- artesian surface
- perched surface
- speleothem
- cone of depression
- A local water table positioned above the regional water table is said to be:
- stranded
- shifted
- perched
- displaced
- depressed
- The most abundant, natural acid is:
- nitric
- carbonic
- hydrochloric
- citric
- sulfuric
- The best aquiclude would have which one of the following pairs of
characteristics?
- low permeability and high porosity
- high permeability and high porosity
- high water content
- high permeability and low porosity
- low permeability and low porosity
- Which one of the following features is a sure sign of karst?
- sinkholes
- flowing wells
- high water content
- cones of depression
- speleothems
Return to the Physical Geology Home Page




