BCHS 3305 Exam
#3 (Answers at end) 11/09/09
Multiple-Choice. Choose one answer for each question. Each correct answer gets two points. Each wrong answer or no answer gets zero
point but no extra penalty.
On the
answer sheet, identify (a) your name AND (b) the last four digits
of your UH student #.
·
The
transport of an acyl carnitine from cytosol to mitochondrial matrix is directly
coupled to the transport of a (#1) ____ from mitochondrial matrix to cytosol by
an antiport system.
[(A) acyl-CoA; (B) CoA;
(C) fatty acid; (D)
carnitine]
·
Carnitine
palmitoyl transferase II is on the surface of the mitochondrial inner membrane
that faces the (#2) ____.
[(A) cytosol; (B) mitochondrial matrix]
·
The
enoyl-CoA metabolite in the pathway of fatty acid b-oxidation
is in the (#3) ____ configuration.
[(A) D2-cis; (B) D2-trans; (C) D3-cis; (D) D3-trans]
·
The
complete oxidation of decanoic acid (CH3-(CH2)8-COOH)
to CO2 and H2O by β–oxidation, TCA cycle, and
oxidative phosphorylation will produce a NET gain of (#4) ____ molecules of
ATP. (Note: GTP is considered the same
as ATP)
[(A) 78; (B) 79; (C) 80; (D) 81; (E) none of the above]
·
The
enzyme enoyl-CoA isomerase (#5) ____ convert the substrate I to the product II.
[(A) can; (B) cannot]

I II
·
The
reaction as shown below (#6) ____ be catalyzed by an isomerase that we have
discussed in our class. [(A) can;
(B) cannot]
![]()
·
The
hydroxy group in the hydroxyacyl-ACP metabolite in normal fatty acid
biosynthesis pathway assumes the (#7) ____ configuration.
[(A) L-a;
(B) L-b; (C)
D-a; (D) D-b]
·
In
ketone body biosynthesis, the hydroxy group of the hydroxybutyrate (derived
from acetoacetate) is in the (#8) ____ configuration.
[ (A) L-a;
(B) L-b; (C)
D-a; (D) D-b]
·
The
enzyme propionyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes the conversion of propionyl-CoA to
the (#9) ____ form of methylmalonyl-CoA.
[(A) S; (B) R]
·
In
fatty acid b-oxidation, the conversion of a
saturated fatty acyl-CoA to enoyl-CoA requires (#10) ____ as a reactant, and
the conversion of hydroxyacyl-CoA to ketoacyl-CoA requires (#11) ____ as a
reactant.
[(A) FAD; (B) FADH2; (C)
NAD+; (D) NADH + H+; (E) none of the above]
·
For
fatty acid biosynthesis in cytosol, the conversion of acetoacetyl-ACP to
hydroxybutyryl-ACP requires (#12) ____ as a reactant, and the conversion of
butenoyl-ACP to butyryl-ACP requires (#13) ____ as a reactant.
[(A) NAD+; (B) NADH + H+; (C)
NADP+; (D) NADPH + H+; (E) none of the above]
·
In
the following reaction catalyzed by b-ketoacyl-ACP synthase one
particular carbon in the reactant malonyl-ACP is labeled with an isotope marker
as indicated by the asterisk. This
carbon will be recovered at position (#14)
____ in the product as shown below.
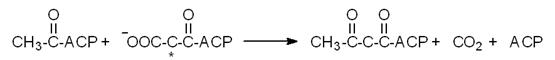
[A B C D E]
·
Following
one cycle of the tricarboxylate transport system as shown below, there will be
a net gain of one molecule of acetyl-CoA and one molecule of (#15) ____ in the
cytosol. Also there will be a net loss
of (#16) ____ in the cytosol.
·
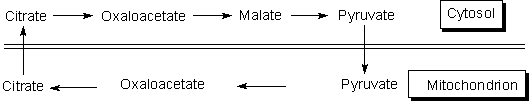
[(A) NAD+ ; (B) NADH; (C)
NADP+; (D) NADPH]
·
For
further elongation of palmitate in mitochondria, all metabolites are activated
in forming a thioester linkage with (#17) ____.
[(A) CoA; (B) ACP]
·
A
desaturase (#18) ____ catalyze the following reaction: [(A)
can; (B) cannot]
![]()
·
Linoleate
(18:2, D9,D12) is an essential fatty acid for
human because human cannot generate (#19) ____ double bond.
[(A) the D9;
(B) the D12;
(C) either the D9 or the D12]
·
The
conversion of β–hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA to mevalonate requires (#20)
____ as co-substrate.
(A) one NADPH; (B)
two NADPH; (C) one NADH; (D)
two NADH; (E) none of the above]
·
The
molecule as shown below is (#21) ____.
[(A) 5-pyrophosphomevalonate;
(B) isopentenyl
pyrophosphate; (C) dimethylallyl pyrophosphate;
(D) none of the above]
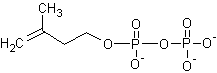
·
The
addition of one farnesyl pyrophosphate to another farnesyl pyrophosphate to
form a squalene is a (#22) ____ condensation reaction.
[(A) head-to-head; (B) head-to-tail]
·
The
conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glycerol-3-phosphate requires (#23)
____, and the conversion of acyl-dihydroxyacetone phosphate to lysophosphatidic
acid requires (#24) ____. [(A) NADH; (B)
NAD+; (C) NADPH; (D) NADP+]
·
Phosphoethanolamine
has to be activated by (#25) ____ before reacting with diacylglycerol to form
phosphatidylethanolamine.
[(A) ATP; (B) CTP]
·
The following molecule (#26) ____
lanosterol. [(A) is; (B) is not]

·
The
excreted end product from the amino group of amino acids is (#27) ____ in
uricotelic animals.
[(A) ammonia; (B) uric acid; (C)
urea]
·
For
the catabolism of amino acids, initially a transamination reaction takes place
between a variety of amino acids and (#28) ____ to form a single amino acid
product for further deamination.
[(A) a-ketobutyrate; (B)
a-ketoglutarate; (C)
acetoacetate]
·
Glutamate
dehydrogenase is an allosteric enzyme with (#29) ____ as an activator, and
(#30) ____ is an inhibitor.
[(A) GMP; (B) GDP;
(C) GTP; (D)
none of the above]
·
The
molecule as shown below is a(n) (#31) _____.
[(A)
aldimine; (B) quinonoid; (C) ketimine]
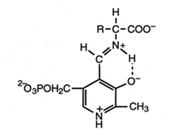
·
Pyridoxine
(#32) ____ an active cofactor for the enzyme aminotransferase.
[(A) is; (B) is not]
·
Serine
dehydratase can catalyze the breakdown of serine to form ammonia and (#33) ____
as products.
[(A) a-ketobutyrate; (B)
a-ketoglutarate; (C)
acetoacetate; (D) pyruvate; (E) none of the above]
·
Eukaryotes
have two forms of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase, namely the mitochondrial CPS
I and the cytosolic CPS II, of which only the (#34) ____ participates in the
synthesis of urea.
[(A) CPS I; (B) CPS II]
·
The
condensation of citrulline and aspartate to form argininosuccinate by the
catalysis of argininosuccinate synthetase is driven by energy derived from the
hydrolysis of(#35) ____.
[(A) ATP ® ADP
+ Pi; (B) ATP ® AMP
+ PPi]
·
Following
the urea cycle, the nitrogen atom in ammonia is preserved in (#36) ____.
[(A) citrulline only; (B) ariginino-succinate only; (C)
urea only; (D) all of the
above; (E) none of A, B, or C]
·
For
the regulation of the urea cycle, enhanced degradation of amino acids will
step-wise lead to (#37) ____ activity of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I.
[(A) a lower; (B) a higher; (C)
no significant change of]
·
The
cellular level of citrulline in cytosol (#38) ____ regulatory role on the
efficiency of urea cycle.
[(A) has a; (B) has no]
·
Following
is a list of catabolites derived from amino acids.
[(A) Acetyl-CoA; (B)
Acetoacetate; (C) Pyruvate; (D) Fumarate; (E)
Succinyl-CoA]
For the known degradation pathway(s) of a
given amino acid, ONE CATABOLITE from the above list will be generated BEFORE
the possible formation of any other catabolites shown above. Choose from the above list to complete the
following statements:
[Example:
Threonine undergoes one degradation pathway to first form A ,
and another pathway to first form C . (Note:
For two answers, list them in alphabetic order.)]
- Phenylalanine
undergoes one degradation pathway to first form (#39) ____, and another
pathway to first form (#40) ____.
- Isoleucine
undergoes one degradation pathway to first form (#41) ____, and another
pathway to first form (#42) ____.
- Methionine
undergoes a single degradation pathway to first form (#43) ____.
·
For
ketone body formation, the enzyme b-hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA lyase
in (#44) ____ converts b-hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA to
acetoacetate.
[(A) cytosol; (B)
mitochondria]
·
The
active one-carbon unit in N5,N10-methylene-THF is at (#45) ____
that in N5,N10-methenyl-THF. (where THF = tetrahydrofolate)
[(A) a higher oxidation state than;
(B) the same oxidation state
as; (C) a lower oxidation state than]
·
The
following molecule is (#46) ____ (where R is –benzoyl-(glutamate)1-6)
[(A) N5-methyl-THF; (B)
N5-formyl-THF; (C)
N5-formimino-THF; (D)
none of the above]
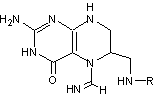
·
The
conversion of glycine to serine requires (#47) ____ as a one-carbon donor.
[(A) N5-methyl-THF; (B)
N5,N10-methylene-THF; (C)
N5,N10-methenyl-THF; (D)
N5-formyl-THF;
(E)
N10-formyl-THF]
·
For
the shortest biosynthetic pathway, (#48) ____ is a precursor for the
biosynthesis of proline, and (#49) ____ is a precursor for the biosynthesis of
asparagine.
[(A) α-Ketoglutarate; (B) 3-Phosphoenolpyruvate; (C)
Oxaloacetate; (D) Pyruvate]
·
For human, tyrosine (#50) ____ an
essential amino acid.
[(A) is; (B) is not]
Answers: (1-D), (2-B), (3-B), (4-B), (5-A), (6-A), (7-D), (8-D), (9-A), (10-A), (11-C), (12-D), (13-D), (14-C), (15-D), (16-B), (17-A), (18-B), (19-B), (20-B), (21-B), (22-A), (23-A), (24-C), (25-B), (26-B), (27-B), (28-B), (29-B), (30-C), (31-A), (32-B), (33-D), (34-A), (35-B), (36-D), (37-B), (38-A), (39-B), (40-D), (41-A), (42-E), (43-E), (44-B), (45-C), (46-C), (47-B), (48-A), (49-C), (50-B)