FATTY ACID OXIDATION |
·
Occurs
in mitochondria.
·
Biological
fatty acids are mostly even number in C.
For unsaturated FAs, the double bonds are mostly cis.
·
Franz
Knoop discovered in 1904: Losing a 2-C unit by oxidation (Fig. 19-9)

|
I.
OXIDATION OF EVEN CHAIN SATURATED FAs |
A. Activation and Entry into Mitochondria by
Carnitine Shuttle
1. Activation on mitochondrial outer membrane and
endoplasmic reticulum by
(Fatty) Acyl-CoA synthetases (or thiokinases)
·
Acetyl-CoA
synthetase: acetate, propionate,
acrylate (C=C-COO-)
·
Medium
chain acyl-CoA synthetase: 4-12 Cs
·

Long-chain acyl-CoA
synthetase: 12-22 Cs or more
The hydrolysis
of PPi by inorganic pyrophosphatase provide the driving energy.
2. Transfer
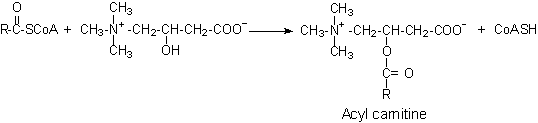
to Carnitine
Acyl-CoA has a limited ability to
cross mitochondrial inner membrane.
·
Carnitine palmitoyl transferase I
(on cytosolic face of
mitochondrial inner membrane)
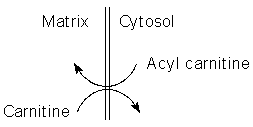
3. Specific transfer of acyl carnitine into mitochondrial
matrix. (see step 2 in Fig. 19-11)
4. Converted back to acyl-CoA by
·
Carnitine palmitoyl transferase
II
(on matrix face of mitochondrial
inner membrane)
Acyl carnitine +
CoASH → Acyl-CoA + Carnitine
5. Transfer of carnitine back to cytosolic side. (Step 4 in Fig. 19-11)
|
b-OXIDATION |
All oxidation enzymes are in
mitochondrial matrix. (See Fig. 19-12)
1. Acyl-CoA
dehydrogenase
·
Produces
trans-Δ2-enoyl-CoA. Note that naturally occurring unsaturated
fatty acids are cis.
·
Has
a bound FAD cofactor.
·
Jamaican
vomiting sickness – eating unripe ackee fruit which contains an unusual amino
acid hypoglycin A, which is a mechanism-based (or suicide) inhibitor against
acyl-CoA dehydrogenase.
2. Enoyl-CoA
hydratase
·
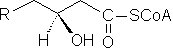
Specifically produces
3-L-hydroxyacyl-CoA from trans-Δ2-enoyl-CoA.
·
Can
also produce 3-D-hydroxyacyl-CoA from cis-Δ2-enoyl-CoA.
3.
3-L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (absolute stereospecificity for
3-L)
4. b-Ketoacyl-CoA
thiolase
|
ENERGETIC
CONSIDERATION |
OXIDATION
OF PALMITATE (16:0)
Palmitate + ATP + CoA →
Palmitoyl-CoA + AMP + PPi (or 2 Pi) - 1 ATP
Palmitoyl-CoA + 7 CoA + 7 FAD + 7
NAD+ + 7 H2O
→
8
Acetyl-CoA + 7 FADH2
+ 7 NADH + 7 H+
7 FADH2 → 14
ATP
7 NADH → 21
ATP
8 Acetyl-CoA → TCA
→ 8 ´ 12 = 96 ATP (Each
TCA cycle → 1 GTP + 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 = 12 ATP)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Σ = 130 ATP
|
OXIDATION OF ODD-NUMBER FAs |
(See Fig. 19-16; in some plants and
marine organisms)
1. R-CO-SCoA
→
→
→
Propionyl-CoA
2. Propionyl-CoA
carboxylase
CH3-CH2-CO-SCoA + ATP + *CO2 + H2O → (S)-Methylmalonyl-CoA + ADP + Pi
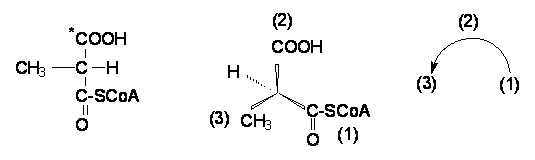
3. Methylmalonyl-CoA
racemase
(S)-Methylmalonyl-CoA ⇌
(R)-Methylmalonyl-CoA
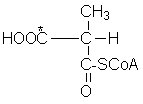
4. Methylmalonyl-CoA
mutase
(R)-Methylmalonyl-CoA ⇌
Succinyl-CoA (HOO*C-CH2-CH2-CO-SCoA)
5. TCA
Cycle
|
OXIDATION OF
UNSATURATED FAs |
See Fig. 19-15.